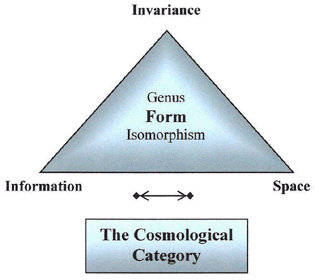
 The last of the three Categories of Philosophy, the Cosmological Category, reflects the nature of the Hermeneutic Category—as did its counterpart: the Ontological Category (for, of course, all are parsed in terms of a Syzygy). At the same time, the Cosmological Category conforms to the findings of Physics, and as a result this Category—called Form, and represented by Information and Space—has its Syzygy fleshed out in terms of the Invariance of Information (or Form) throughout all of Space. According to modern Physics, this symmetry of Space gives rise to all physical stabilities that derive from the conservation properties of Space itself. The last of the three Categories of Philosophy, the Cosmological Category, reflects the nature of the Hermeneutic Category—as did its counterpart: the Ontological Category (for, of course, all are parsed in terms of a Syzygy). At the same time, the Cosmological Category conforms to the findings of Physics, and as a result this Category—called Form, and represented by Information and Space—has its Syzygy fleshed out in terms of the Invariance of Information (or Form) throughout all of Space. According to modern Physics, this symmetry of Space gives rise to all physical stabilities that derive from the conservation properties of Space itself.
 These spatial symmetries are related to the concept of Duality (as, in fact, is symmetry in general), which has recently been recognized as being a fundamental concept. In Logic, which lies at the foundation of all Western knowledge, Duality is a fundamental Form. And in Physics, all elementary components (with exception of the Higgs Boson) participate in the dance of wave and particle dualities. From the photon to the primary Quarks—u and d, Up and Down—and the primary Leptons—e and n, the Electron and the Neutrino—not to mention their Antimatter counterparts—the Positron and the anti-quarks—everything is dualistic. Consequently we must admit that the dichotomy embodied in this Duality of our theories of Quantum Fields lies at the heart of all physical systems, and this includes the largest structures as well as the smallest. Such articles as the December 1994 Scientific American article The Duality in Matter and Light and the January 1996 article Explaining Everything underscore this point. These spatial symmetries are related to the concept of Duality (as, in fact, is symmetry in general), which has recently been recognized as being a fundamental concept. In Logic, which lies at the foundation of all Western knowledge, Duality is a fundamental Form. And in Physics, all elementary components (with exception of the Higgs Boson) participate in the dance of wave and particle dualities. From the photon to the primary Quarks—u and d, Up and Down—and the primary Leptons—e and n, the Electron and the Neutrino—not to mention their Antimatter counterparts—the Positron and the anti-quarks—everything is dualistic. Consequently we must admit that the dichotomy embodied in this Duality of our theories of Quantum Fields lies at the heart of all physical systems, and this includes the largest structures as well as the smallest. Such articles as the December 1994 Scientific American article The Duality in Matter and Light and the January 1996 article Explaining Everything underscore this point.
|

