Most Probable Number (MPN) Presumptive Test
The MPN test is a statistics-based test which estimates the number of fecal coliforms in a water sample based on the degree of lactose fermentation by organisms in the sample. In this test, a series of tubes of phenol red lactose broth are inoculated with measured amounts of water to determine if the water contains any lactose-fermenting bacteria that produce gas.
If, after incubation, fermentation plus gas production is demonstrated, it is presumed that coliforms are present in the water sample. By counting the number of positive tubes positive at each dilution, the “most probable number” (MPN) of coliforms is statistically determined using a standardized chart.

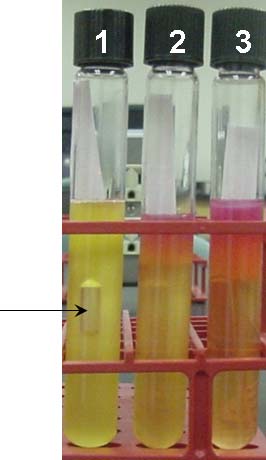
Tube #1: Positive for fecal coliforms. Note (1) the gas present in the Durham tube and (2) the color change from red to yellow as acid end-products react with the pH indicator.
Tube #2: Negative for fecal coliforms. Note the absence of gas in the Durham tube. Even though the pH indicator has changed from red to yellow, gas must be produced for a positive result.
Tube #3: Negative for fecal coliforms.