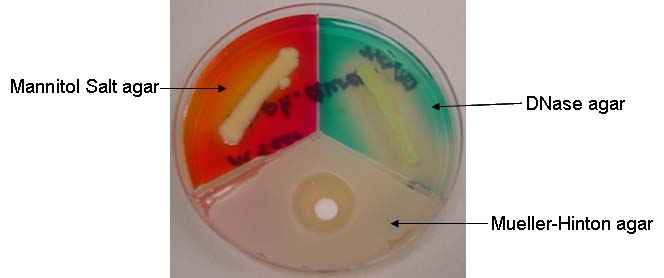
Staphylococcus Tri-Plate
Staphylococcus species are identified using a Staph tri-plate containing 3 types of microbiological media: (1) Mannitol Salt Agar (2) DNase agar and (3) Mueller-Hinton agar.
Mannitol Salt Agar: MSA is both selective and differential. It contains 7.5% NaCl, which selects for organisms which are halotolerant. The media also contains mannitol and phenol red, which allows differentiation of organisms based on whether or not they are able to ferment mannitol. If mannitol is fermented, the acidic fermentation products react with the phenol red pH indicator, which changes color from red to yellow.
DNase agar: DNase agar contains an emulsion of DNA, peptides, and methyl green dye. The dye and polymerized DNA form a complex that gives the agar a blue-green color at pH 7.5. Bacterial colonies that produce DNase will hydrolyze the DNA in the medium into smaller fragments unbound from the methyl green dye. This results in clearing around the bacterial growth.
Mueller-Hinton agar: M-H agar is a type of nutrient agar standardized for use in antimicrobial testing. The levels of thymine, thymidine, calcium ions and magnesium ions are controlled in this medium so as not to interfere with susceptibility testing. The M-H agar will be used to test susceptibility to the antibiotic Novobiocin.

The organism on this plate is positive for mannitol fermentation, positive for DNase production, and susceptible to the antibiotic Novobiocin.